How to Read Nutrition Labels for Better Blood Pressure Control
Managing high blood pressure isn’t just about cutting back on salt—it’s about understanding the importance of nutrition and making informed choices at every meal. One of the simplest and most effective tools to support your health and nutrition goals is the nutrition label found on packaged foods. Learning how to read and understand this information can empower you to take better control of your blood pressure and overall well-being.
Here’s a quick guide to help you decode nutrition labels and make heart-smart decisions every time you shop or eat.
1. Start with the Serving Size
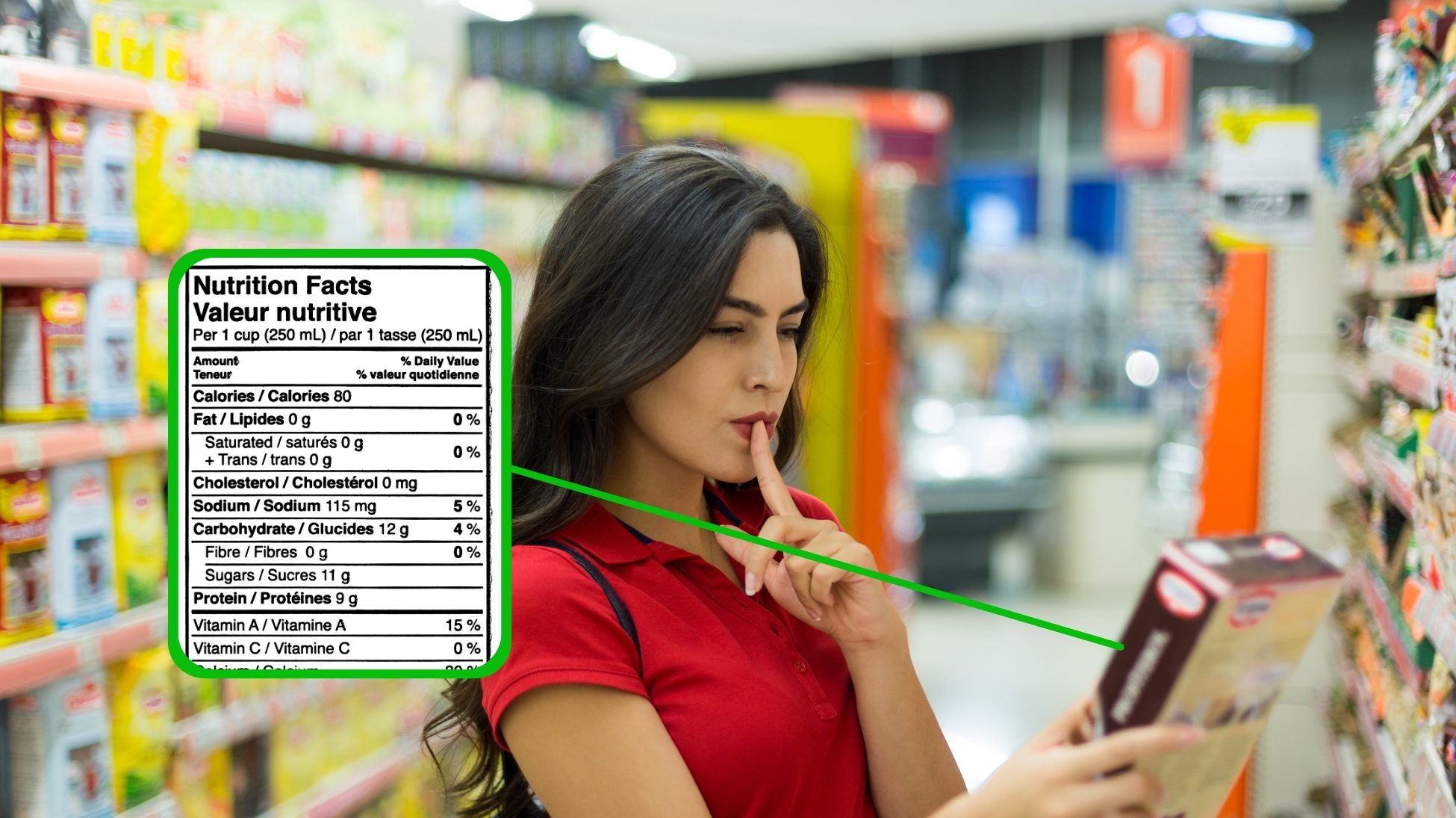
When learning about nutrition, it’s essential to start with the serving size and servings per container. All the nutrient information on the label is based on this serving size. Eating more than the serving size means you’ll also consume more sodium, calories, and other nutrients than you might expect.
For example, if a soup can lists 400 mg of sodium per serving but the can contains two servings, eating the whole can means 800 mg of sodium.
2. Check the Sodium Content
One of the biggest factors affecting blood pressure is sodium. Understanding how to monitor sodium intake is a key part of health and nutrition. High sodium levels can cause fluid retention and raise blood pressure. The American Heart Association recommends keeping sodium intake between 1,500–2,300 mg per day, especially if you have hypertension.
Look for foods labeled:
Low sodium: 140 mg or less per serving
Very low sodium: 35 mg or less
Sodium-free: Less than 5 mg
Processed and packaged nutrition food often contain high sodium, so always check the label carefully.
3. Look for Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral that helps balance the effects of sodium and supports healthy blood pressure. While not always listed, some nutrition labels include potassium amounts. Foods rich in potassium include bananas, spinach, beans, and potatoes. When available, choose products with at least 10% of the Daily Value (DV) of potassium.
4. Watch Out for Saturated Fats and Trans Fats
Alongside sodium, the importance of nutrition for heart health means paying attention to fats. Saturated fats and trans fats contribute to clogged arteries and increase cardiovascular risk.
Opt for foods with:
Low saturated fat: Less than 1.5g per serving
No trans fat: Avoid products listing “partially hydrogenated oils” in the ingredients.
5. Don’t Be Fooled by “Healthy” Claims
Labels may include terms like “low fat,” “gluten-free,” or “natural,” but these don’t always guarantee a product supports heart health. When choosing nutrition food, always read the full nutrition label and ingredient list. Some “healthy” products may still contain high sodium or added sugars.
6. Use the Percent Daily Value (%DV) Wisely
The %DV on nutrition labels shows how much a nutrient in one serving contributes to your daily intake, based on a 2,000-calorie diet. For sodium, aim for 5% DV or less per serving to manage blood pressure. A product with 20% DV or more is considered high.
Understanding how to read nutrition labels is a valuable skill that highlights the benefits of nutrition in managing blood pressure and maintaining heart health. By focusing on serving sizes, limiting sodium and unhealthy fats, and choosing foods rich in beneficial nutrients like potassium and fiber, you can make smart choices that support your well-being.

If you want expert guidance about nutrition tailored to your lifestyle, Halcyon Nutrition offers personalized plans to help you build sustainable habits. Our certified nutritionists and dietitians work closely with you to improve your food choices and help you experience the full benefits of nutrition for better blood pressure and overall health.
Sharing is caring!


